Georgian Alphabet
Overview from Omniglot:
Origin
Armenian is an Indo-European language spoken mainly in Armenia (Հայաստան [Hayastan]) and in Nagorno-Karabakh, a de facto, though unrecognised, independent republic in the Nagorno-Karabakh region of the South Caucasus. This area is also known as the Republic of Artsakh (Արցախի Հանրապետություն), and is recognised internationally as part of Azerbaijan. There are also Armenian speakers in many other countries, including Russia, Lebanon, the USA, Georgia, Iran, France, Syria, Turkey, Iraq, Uzbekistan and Ukraine.
Armenian belongs to its own independent branch of the Indo-European language family. It is not closely related to any other languages.
There are two main varieties of Armenian: Eastern Armenian (արևելահայերեն) and Western Armenian (արեւմտահայերէն). To educated speakers of either variety the other is more or less mutually intelligible.
Eastern Armenian has 2.9 million speakers in Armenia, where it is the official and most commonly-spoken language. There are also about 660,000 speakers of Eastern Armenian in the Dagestan Republic of the Russian Federation, 120,000 in Azerbaijan, and 100,000 in Iran. The total number of speakers is about 3.8 million [source].
The largest concentrations of Western Armenian speakers are found in Lebanon (294,000), the USA (238,000), Georgia (150,000), Armenia (73,000), France (70,000), Syria (65,000), Turkey (61,000), Iraq (60,000), Uzbekistan (60,000) and Ukraine (50,000). The total number of speakers is about 1.2 million [source].
Armenian is the offical language of Armenia and Nagorno-Karabakh, and has official status as a minority language in Cyprus, Hungary, Iraq, Poland, Romania and Ukraine. Until the the early 1990s schools in Armenian taught in either Armenian or Russian, however after the collapse of the USSR, Armenian became the main medium of instruction and the Russian-medium schools were closed. In 2010 Russian language education was reintroduced in Armenia.
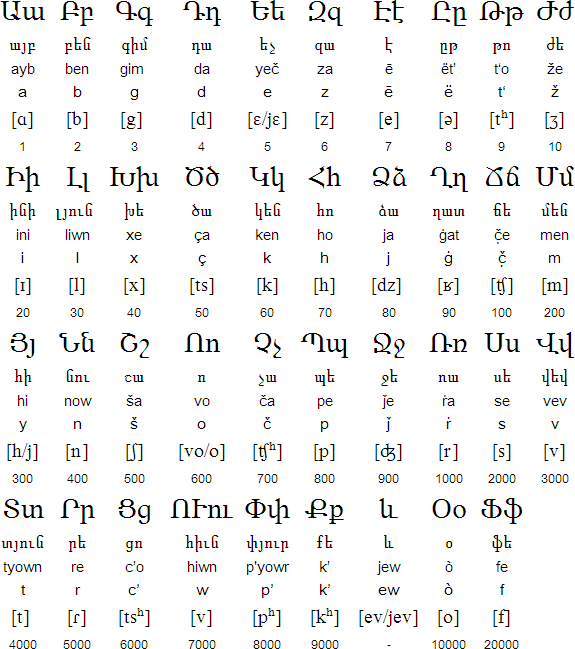
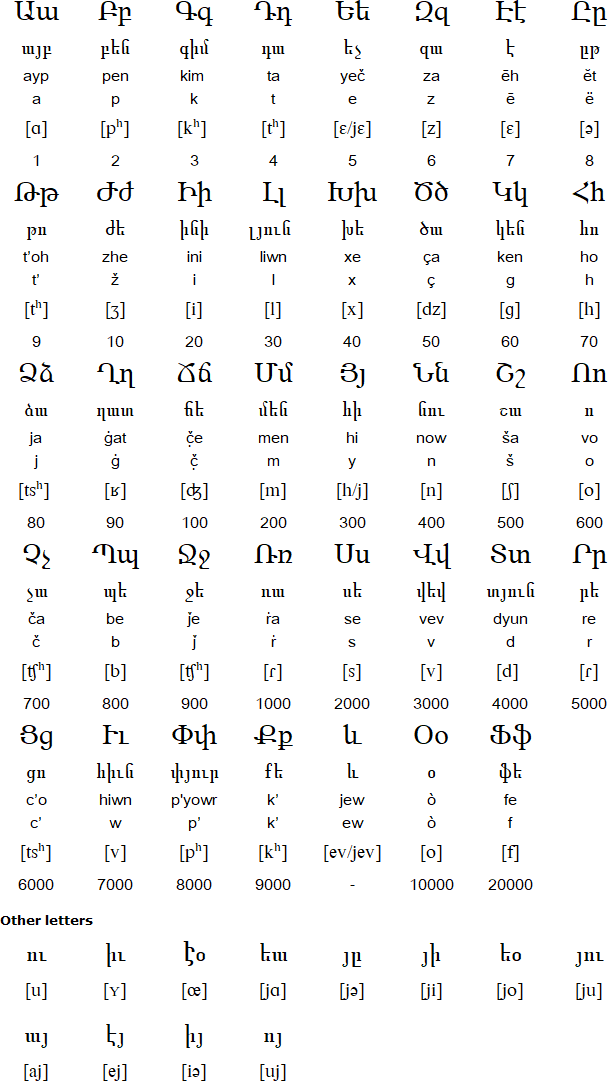
Notable features
- Type of writing system: alphabet
- Writing direction: left to right in horizontal lines
- Used to write: Armenian, and formerly used for Turkish, Azeri, Kipchak and Kurdish
- There are a few minor differences in the pronunciation of the letters between the two standard literary forms of Armenian: Western and Eastern.
- Most of the letters have numerical values.
Online Resources- Dictionaries and Spellcheckers
University of California, Berkeley: Armenian Language and Culture
This guide to Armenian language and culture offers resources that will be of interest to students and instructors hoping to find more materials on Armenian language and culture. This guide features sections on Armenian manuscripts, newspapers, digital collections, and topical books and journals.
Note: copyright statement. Contact the compilers for any reproduction inquiries.

